FPV (First-Person View) drones have become increasingly popular in recent years, with enthusiasts and professionals alike seeking to capture stunning aerial footage and experience the thrill of immersive flight. One crucial aspect of building or purchasing an FPV drone is the frame material, which must strike a delicate balance between durability and weight. In this article, we will explore the various materials used in FPV drone frames, their characteristics, and the trade-offs involved in selecting the ideal material for your drone.
Carbon Fiber: The Gold Standard
Carbon fiber is widely regarded as the gold standard for FPV Drone due to its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. This lightweight material is incredibly resistant to damage, able to withstand the rigors of high-speed flight and minor crashes. Carbon fiber frames are also highly rigid, which helps to maintain the drone’s structural integrity and prevent vibration-induced damage to sensitive components. However, high-quality carbon fiber frames can be expensive, and the material’s brittleness means it may shatter or crack upon impact, requiring costly repairs.
Aluminum: A Durable Alternative
Aluminum is another popular material for FPV drone frames, offering a more affordable alternative to carbon fiber. Aluminum frames are often heavier than their carbon fiber counterparts but provide excellent durability and resistance to damage. The material’s ductility also means it can absorb impacts without shattering, reducing the likelihood of costly repairs. However, aluminum frames may be more prone to vibration and flexing, which can affect the drone’s overall performance and stability.
Titanium: The High-End Option
Titanium is a high-end material used in some FPV drone frames, offering an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and unparalleled durability. Titanium frames are incredibly resistant to corrosion and fatigue, making them ideal for drones that will be flown in harsh environments or subjected to extreme stress. However, titanium is also one of the most expensive materials used in drone construction, making it inaccessible to many enthusiasts.
Fiberglass and Other Composites
Fiberglass and other composite materials are often used in entry-level FPV drone frames or as a budget-friendly alternative to carbon fiber. These materials offer a reasonable balance of durability and weight, although they may not be as rigid or resistant to damage as higher-end options. Fiberglass frames are also more prone to vibration and may require additional reinforcement to maintain the drone’s structural integrity.
Hybrid Frames: The Best of Both Worlds
Some manufacturers have begun to experiment with hybrid frames, combining different materials to achieve an optimal balance of durability and weight. For example, a frame may use carbon fiber for the main structure and aluminum for the arms or other components. Hybrid frames offer a promising solution for enthusiasts seeking high-performance without the hefty price tag associated with high-end materials.
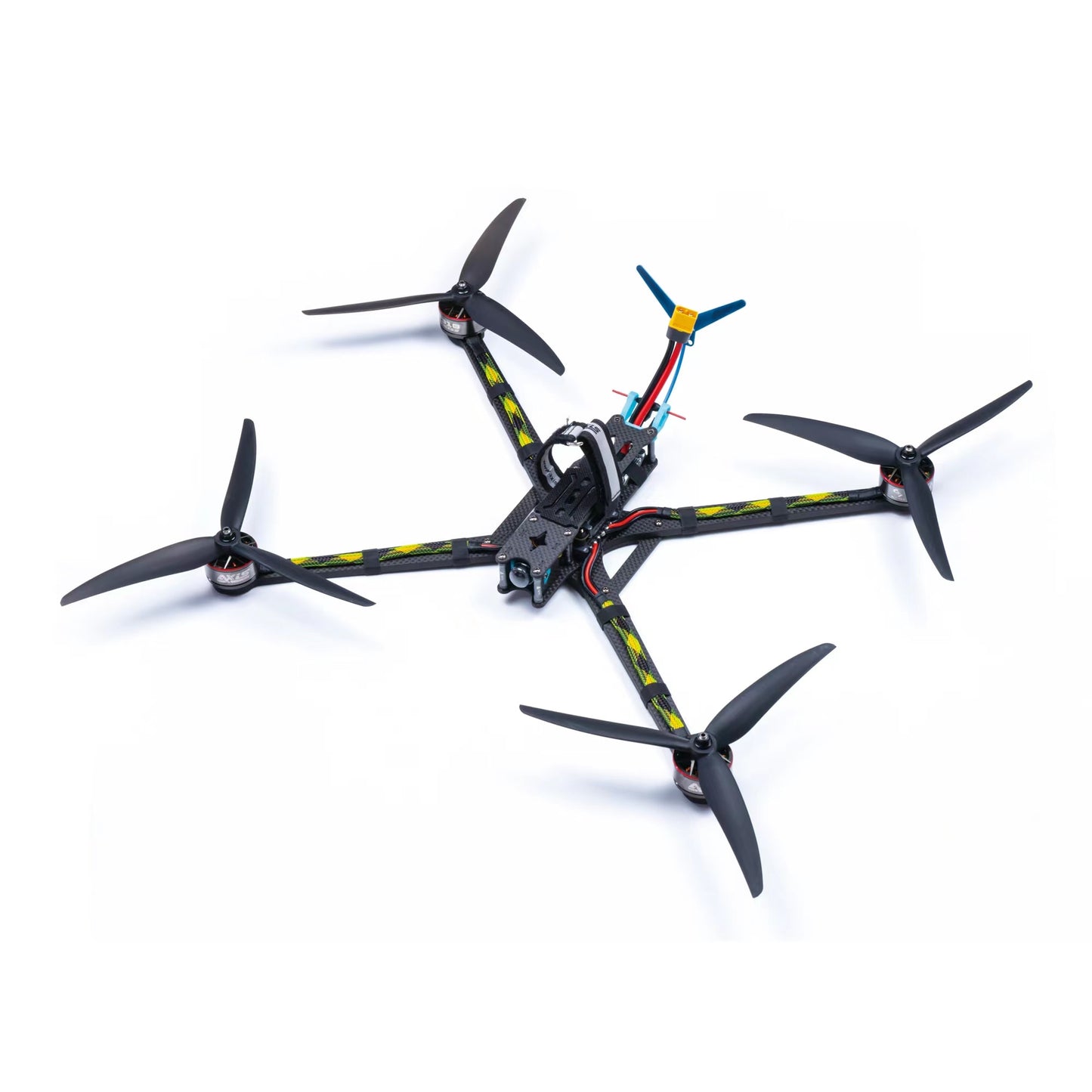

Design and Construction Considerations
When selecting an FPV drone frame, it’s essential to consider the design and construction of the frame, as well as the materials used. A well-designed frame with a robust structure and secure component mounting can help to mitigate the effects of minor crashes and reduce the likelihood of damage. Additionally, the frame’s weight distribution and balance can significantly impact the drone’s overall performance and stability.
Conclusion
Choosing the ideal FPV drone frame material depends on a variety of factors, including budget, flying style, and personal preferences. While carbon fiber remains the gold standard for high-performance drones, other materials like aluminum, titanium, and fiberglass offer viable alternatives for enthusiasts seeking a more affordable or durable option. As the FPV drone community continues to evolve, we can expect to see innovative new materials and designs that further push the boundaries of what is possible in drone construction. By understanding the characteristics and trade-offs of each material, enthusiasts can make informed decisions when selecting or building their next FPV drone.